The Importance of Software Management in Modern IT Environments
1. Introduction
Software has become the backbone of business operations. From basic productivity applications to advanced engineering, manufacturing, and cybersecurity tools, organizations depend on hundreds of software products every day. With this growth comes the critical need for structured Software Management—a process that ensures the right software is purchased, deployed, maintained, audited, and retired efficiently.
2. What Is Software Management?
Software Management is the practice of tracking and controlling the entire lifecycle of software assets across an organization. It includes licensing, usage monitoring, compliance enforcement, renewals, installations, access controls, and cost optimization.
When done correctly, it reduces overspending, improves security, and strengthens IT governance.
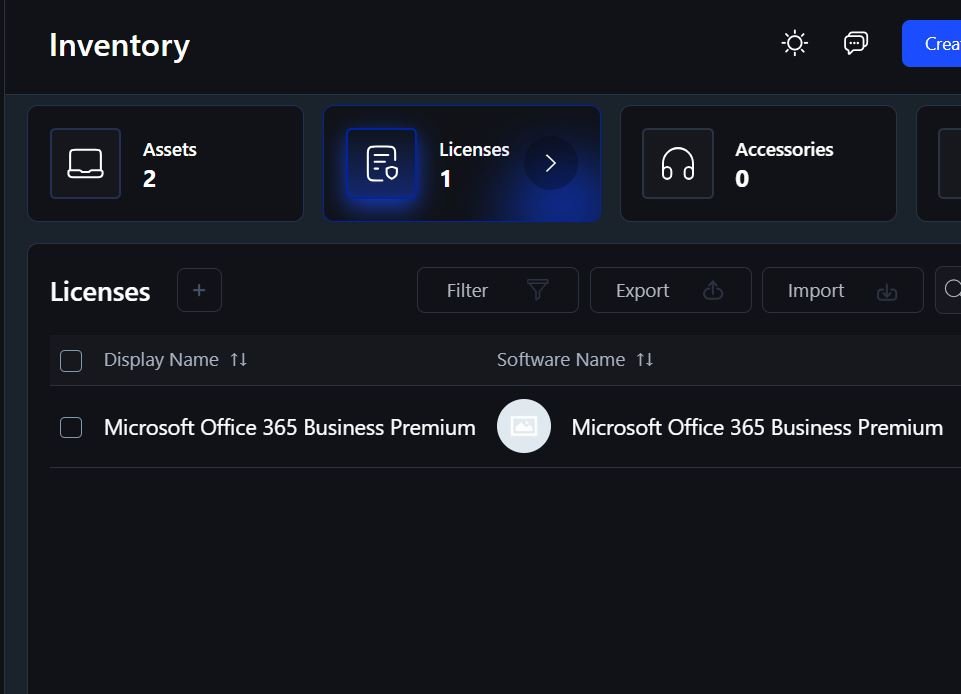
3. Centralized Software Inventory
A major challenge for IT teams is visibility. Many organizations don’t know:
- How many software licenses they own
- Where the software is installed
- Which employees are using which tools
- What versions are deployed
A centralized inventory solves this by creating a single source of truth for all software assets. Accurate records help eliminate unapproved installations and ensure only licensed versions are in use.
4. License Tracking & Compliance
Software vendors frequently audit organizations, and non-compliance can lead to heavy penalties. Proper Software Management ensures:
- Licenses are assigned correctly
- Teams are not using more seats than purchased
- Old versions are updated
- Unauthorized or pirated software is removed
- Compliance reports are readily available
By maintaining clean records, companies avoid surprises during vendor audits and stay aligned with legal requirements.
5. Cost Optimization & Budget Control
Without monitoring, organizations often overspend 20–30% on software. Common issues include:
- Paying for unused or rarely used licenses
- Buying duplicate tools across departments
- Missing renewal dates leading to penalty fees
- Purchasing applications that already exist internally
Effective Software Management identifies these gaps and enables budget planning based on real usage. IT and finance teams gain control over spend and avoid unnecessary purchases.
6. Renewal & Contract Management
Managing renewals is one of the most overlooked areas. Missed renewals can cause downtime, user disruption, or data loss.
A structured renewal process helps track:
- Contract expiry dates
- Subscription renewals
- Version upgrades
- AMC and maintenance schedules
Automated reminders ensure no renewal slips through the cracks.
7. Software Deployment & Access Governance
Unauthorized software installations are a major cybersecurity threat. Proper management involves:
- Defining who is allowed to install software
- Blocking unapproved applications
- Enforcing department-level access
- Linking licenses to users or devices
This controls software sprawl and reduces security risks across endpoints.
8. Software Lifecycle Integration
Software has a lifecycle similar to hardware: procurement → deployment → usage → maintenance → retirement.
Integrating these stages ensures:
- Smooth onboarding/offboarding
- Proper version control
- Clean decommissioning
- Historical audit data
This ensures every software asset delivers full value during its lifespan.
9. Conclusion
Software Management is essential for operational efficiency, financial control, and cybersecurity. With rising software complexity and costs, organizations must adopt structured practices that provide visibility, compliance, and optimization across the entire software portfolio. Companies that implement strong Software Management gain better governance, reduced expenses, and improved productivity.